


| Pair Name | Quercetin, Doxorubicin | ||
| Phytochemical Name | Quercetin (PubChem CID: 5280343 ) | ||
| Anticancer drug Name | Doxorubicin (PubChem CID: 31703 ) | ||
| Structure of Phytochemical |
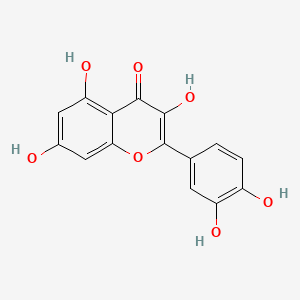
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Structure of Anticancer Drug |
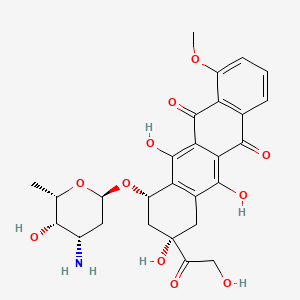
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Pair Name | Quercetin, Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->ROS accumulation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MYC | hsa4609 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| In Vivo Model | Into the right hind limb of each nude mouse, 2×10⁶ 4 T1 TNBC cells were injected subcutaneously. One week later, the mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 3): control group (0.9% saline); Que group (50 mg/kg Que); AC group (5 mg/kg Dox plus 50 mg/kg Cyc); and AC plus Que group (5 mg/kg Dox plus 50 mg/kg Cyc plus 50 mg/kg Que). | |||
| Result | Que could attenuate AC-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting ROS accumulation and activating ERK1/2 pathway in cardiomyocytes, but interestingly, Que could enhance the antitumor activity of AC by inhibiting ROS accumulation and ERK1/2 pathway in TNBC cells. In addition,in vivo studies further confirmed that Que could enhance the chemotherapeutic effect of AC against TNBC while it reduced the injury of cardiotoxicity induced by AC | |||
| Pair Name | Quercetin, Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | ABCB1 | hsa5243 |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Result | These findings demonstrated that quercetin is important in MDR and may be developed into a new reversal agent for cancer chemotherapy. | |||
| Pair Name | Quercetin, Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A60.Z] | Acute myeloid leukemia | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | ABCB1 | hsa5243 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP8 | hsa841 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP9 | hsa842 | |
| In Vitro Model | K-562 | Blast phase chronic myelogenous leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Result | These findings demonstrated that quercetin is important in MDR and may be developed into a new reversal agent for cancer chemotherapy. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quercetin attenuates the cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide regimen and potentiates its chemotherapeutic effect against triple-negative breast cancer. Phytother Res. 2022;36(1):551-561. doi:10.1002/ptr.7342 | Click |
| 2 | Quercetin potentiates the effect of adriamycin in a multidrug-resistant MCF-7 human breast-cancer cell line: P-glycoprotein as a possible target. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1994;34(6):459-64. doi: 10.1007/BF00685655. | Click |
| 3 | Quercetin enhances adriamycin cytotoxicity through induction of apoptosis and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in multidrug-resistant leukemia K562 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jan;11(1):341-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2734. | Click |
